Symptoms of schizophrenia that should be watched closely
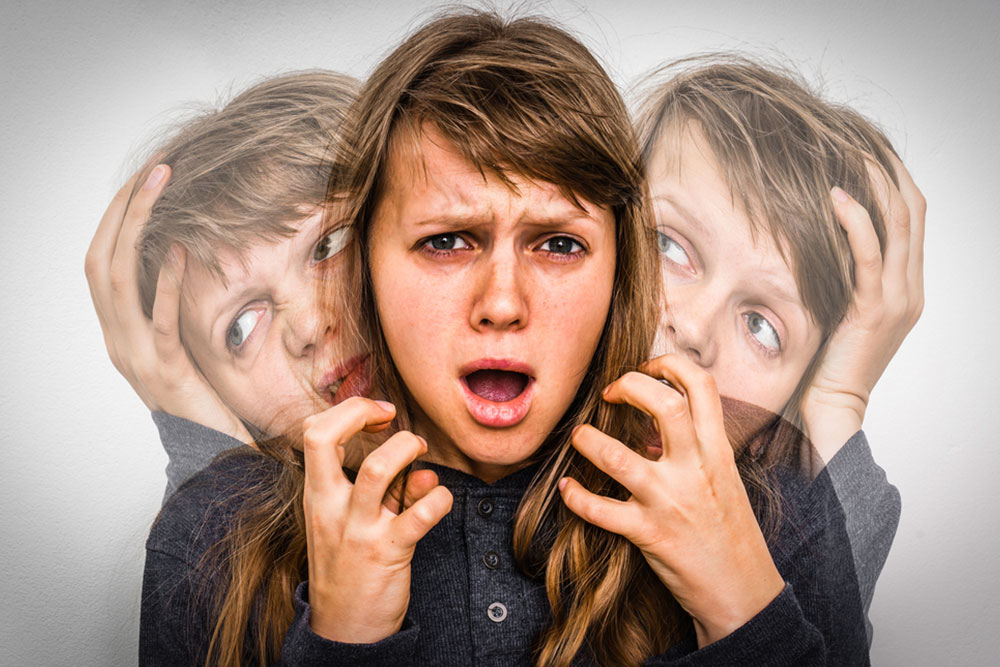
Schizophrenia is a serious neurochemical imbalance, and it completely distorts the way a person thinks and acts. How does one identify the symptoms?
It is wise to know that the first sign of schizophrenia could vary between genders. Men are known to show these symptoms in their late teens or in their twenties whereas women are susceptible anywhere between their twenties and thirties. The prodromal period is a vital stage to be aware of. It is the period between the first occurrence of symptoms and the onset of what is called the schizophrenic episode (technically referred to as psychosis).
The prodromal period does not have a specific start and end date. It could be just a few hours or it could be weeks or years. When it comes to schizophrenia, identifying the trigger points could be difficult in many cases. The period is always accompanied by change in the behavior; it could also indicate subtle changes initially. When boys develop schizophrenia in their teens, significant changes can be observed, some of which could be changes in grades, withdrawal from social activities, lower attention span, temper flareups, and insomnia.
The symptoms can be classified into three:
- Positive symptoms
- Cognitive symptoms
- Negative symptoms
Positive symptoms: In this instance, the word “positive” refers to the fact that it is “good.” The symptoms are not based out of reality and are also known as psychotic symptoms. Examples include delusions, hallucinations, and catatonia. The person has a total inability to think clearly and respond accordingly. Some examples would be:
- Conversation that does not make any sense. Usage of words that have no connection to what is spoken.
- Shifting topics or thoughts rapidly without any logical connections between them
- Slowed movement
- Inability to make decisions
- Unable to relate to senses like sight or sound or touch
- Forgetting frequently
Cognitive symptoms: As the term suggests, these type of symptoms are linked to cognition. The inability to perceive or to store information and to recall are some of the symptoms. Examples include:
- Inability to assimilate and understand information in order to make decisions
- Trouble paying attention
- Poor memory where they are unable to recall any data
Negative symptoms: These type of symptoms display the lack or absence of some of the normal behavior that people otherwise express. Some of them include:
- Highly limited range of emotions
- Withdrawal from family, friends, and other social activities. They also withdraw from their closest kin.
- Ability to communicate is reduced
- Energy levels decrease
- Total lack of motivation including loss of interest in life
- Compromised personal hygiene
Who can get schizophrenia?
Anyone can. It is to be noted that schizophrenia in children is quite rare. It is usually developed after adolescence and affects men at a much younger age than women. About 2.2 million Americans are believed to have schizophrenia; it is also believed that 1% of the population develops schizophrenia. This neurological imbalance in the brain does not restrict itself to race and culture. Consult a neurologist for immediate management if you observe these symptoms in you or a friend.